Snoring happens when airflow is partially blocked as it moves through the nasal passages during sleep, causing vibrations in the throat tissues that produce the sound of snoring. This blockage may be influenced by physical structures, daily habits, or conditions like obstructive sleep apnea, which can interrupt sleep and pose health risks. Understanding the causes of snoring helps determine its severity and how to address it. So, why do people snore? Let’s explore the details in the following article from CLM Sleep.
What happens when you snore?
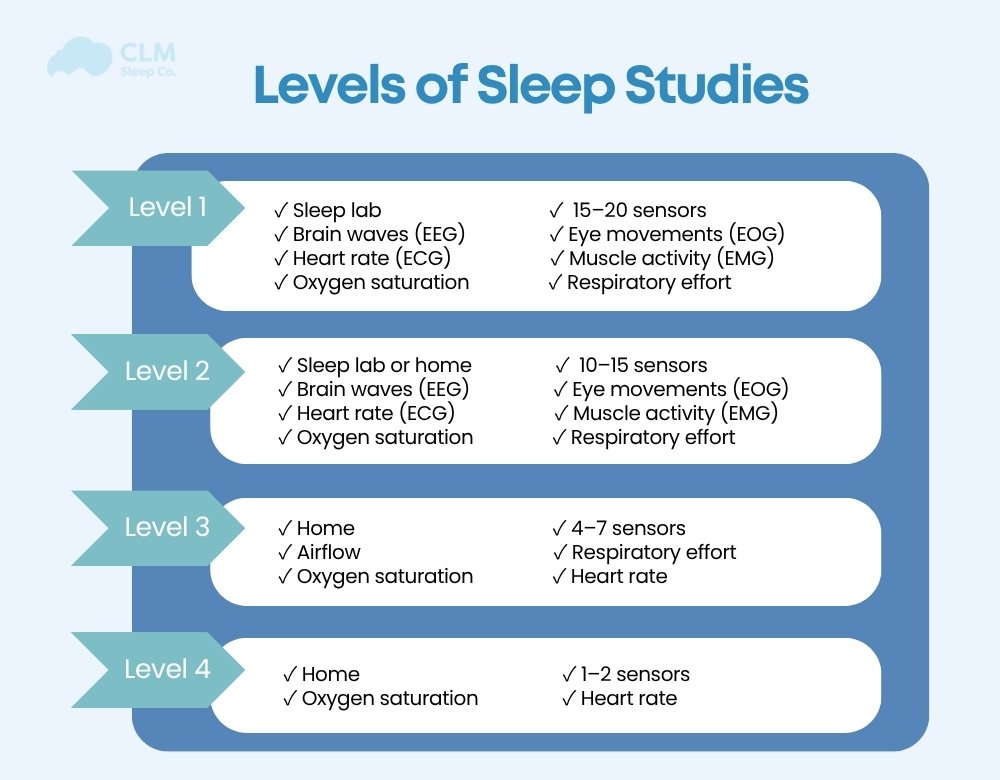
Snoring occurs when the muscles in your soft palate, tongue, and the back of your throat relax. These muscles tend to fall backward into the throat as you fall asleep. While everyone’s throat muscles relax during sleep, sometimes they relax too much, causing the upper airway to narrow and making it harder for air to flow to the lungs. When the airway becomes restricted, the increased airflow pressure causes stronger vibrations, making the snoring sound more pronounced. Although snoring can be very LOUD, you are often unaware you are doing it.
See more:
Snoring in Children: Causes and Solutions
How To Stop Snoring Woman
What causes snoring
Why do people snore? Snoring can be caused by various factors, including the anatomical structure of the mouth and sinuses, alcohol consumption, allergies, colds, and body weight…
As mentioned above, when you transition from light to deep sleep, your soft palate, tongue, and throat muscles relax. When these throat tissues relax, they can partially block the airway and cause vibrations. The narrower the airway, the stronger the airflow passing through, which increases the tissue vibrations, making the snoring sound louder.
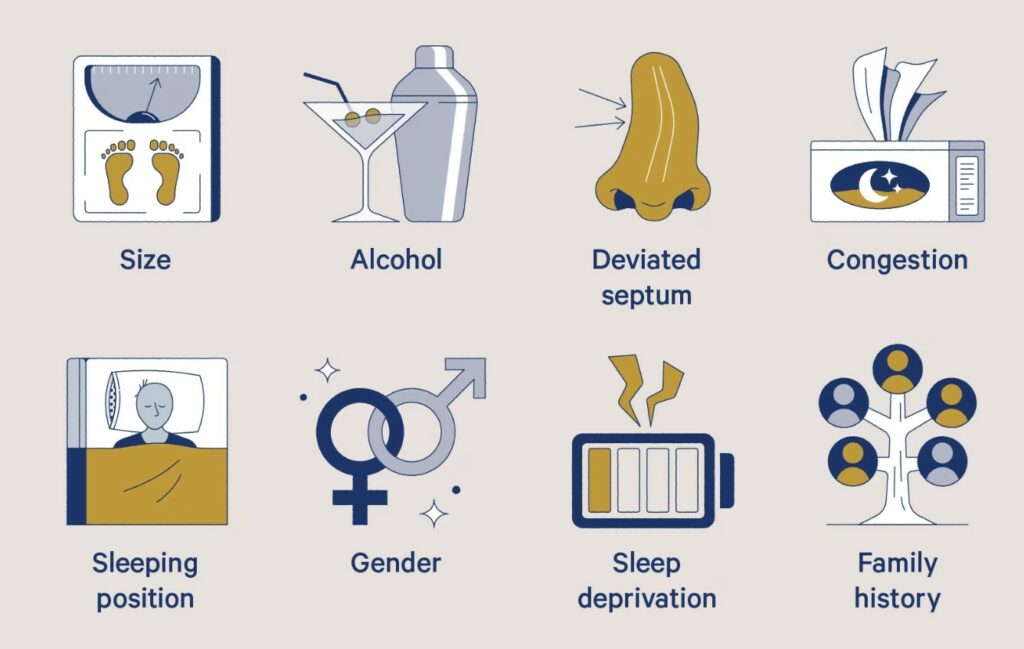
The following factors can affect the airway and contribute to snoring:
Obstruction in the Airway
Obstruction in the airway is one of the key explanations for why people snore. When the airway is partially blocked during sleep, airflow becomes restricted, causing the tissues around the throat to vibrate and produce the sound of snoring. This obstruction can stem from various causes, including:
- Nasal Congestion: Allergies, colds, or sinus infections can narrow the nasal passages, forcing air to flow through a smaller space, leading to snoring.
- Enlarged Tissues: Enlarged tonsils, adenoids, or excessive tissue in the throat, especially in children, can obstruct airflow.
- Obesity: Excess fat around the neck can narrow the airway, increasing the risk of obstruction.
- Excessively Relaxed Throat Muscles: Alcohol, sedatives, or deep sleep can cause the throat muscles to relax too much, obstructing airflow.
- Deviated Septum: Structural abnormalities in the nose, such as a deviated septum, can also restrict airflow and cause snoring.
Age and Muscle Tone
Age and Muscle Tone are two significant factors that can contribute to snoring. As people age, their bodies undergo various changes that affect sleep and breathing:
- Loss of Muscle Tone: Increasing age is frequently associated with a loss of muscle tone, both in the upper airway and most musculature. For example, the soft palate becomes more likely to vibrate at the back of the throat, and the movement of different tissues, including the uvula, causes the sound of snoring that we hear. The same is true for why do old people snore.
- Thinning Tissues: The throat’s tissues can thin with age and decrease their firmness. These more fluctuant tissues tend to vibrate more during the passage restriction of the airflow, therefore snoring more loudly.
- Changes in Sleep: Changes in sleep architecture commonly occur with age in older adults, manifested by reduced deep sleep. Conversely, light sleep tends to bring about a relatively high number of wakenings and more time spent in the lighter stages— a scenario that could enhance snoring.
- Weight Gain: Aging may also result in weight gain, especially around the neck area, which narrows the airway and increases snoring.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal changes, particularly in women during and after menopause, can result in increased fat accumulation in the neck and changes in muscle tone, which can contribute to snoring.
Sleep Position
Your sleep position can significantly affect how much you snore. When lying on your back, the tissues in your throat may easily fall into the airway, causing the tongue to relax more and worsening airway obstruction.
Switching to a side-sleeping position can help reduce obstruction and improve breathing. A body pillow can help you maintain a stable side-sleeping position more effectively.

See more: The Best Sleeping Position
Alcohol and Medication Use
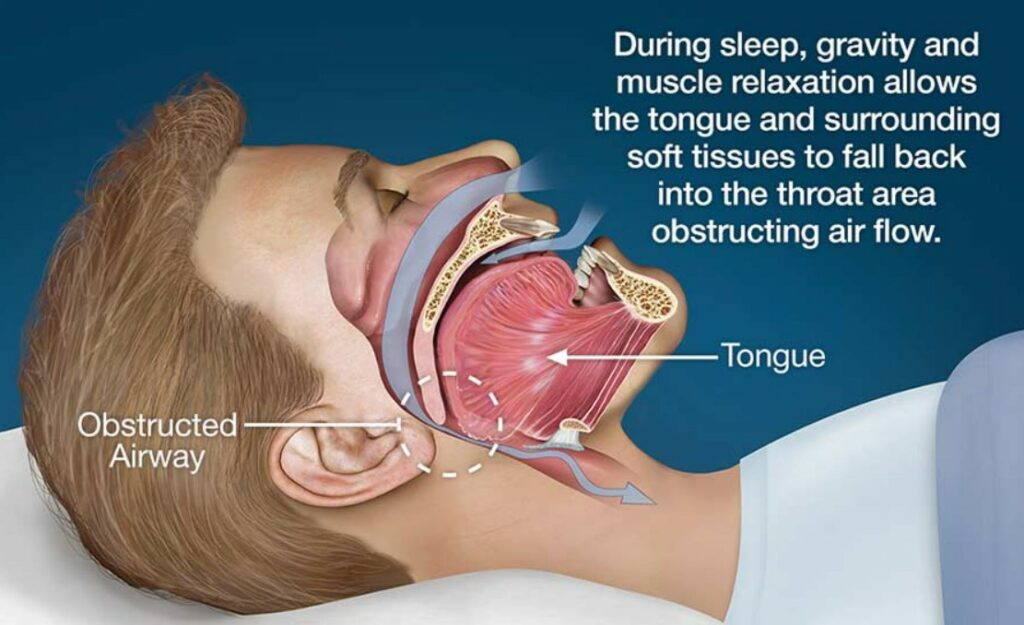
When drinking alcohol, the muscles in the airway relax, slightly blocking airflow. Air has to push through the narrow airway, creating a snoring sound due to increased respiratory resistance. While sleeping, normal resistance doubles, but for those who snore, it increases fourfold. Alcohol can increase this resistance by four to five times, and if a person already snores, resistance can rise up to eight times.
The muscles at the back of a drunk person’s throat close faster than those in a sober person, explaining why do drunk people snore or why louder snoring often happens after drinking. The more alcohol consumed, the more relaxed the tissues and muscles become, leading to even louder snoring.
Besides, using muscle relaxants or sedatives can also lead to snoring. These substances include sleeping pills, antihistamines, and painkillers (especially narcotics). They relax the throat muscles, obstruct airflow, and are a common reason why people snore.
Anatomical Factors
From an anatomical perspective, enlarged tonsils, adenoids, or a large tongue can obstruct airflow through the nose and mouth, making breathing more difficult. A deviated septum (when the cartilage that divides the nostrils is misaligned) can also block airflow, further contributing to breathing difficulties and snoring.
Smoking
Why do people snore? Smoking can affect sleep by causing inflammation in the tissues of the upper airway, which narrows the airflow. This inflammation triggers the production of excess mucus to protect the irritated area. As the airway narrows, air must move through a tighter space, creating vibrations that lead to snoring.
Health Risks Associated with Snoring
Snoring is not just an annoyance; it can also be a sign of serious health issues, particularly obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and cardiovascular diseases. Awareness of these risks is essential for early intervention.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
OSA is severe because airflow completely ceases despite an effort to breathe; airway blockage leading to pauses in breathing is referred to as obstructive apnea. This is commonly associated with snoring, often quite loudly, with periods of silence when airflow is reduced or absent; gasps or choking sounds may occur.
Key Impacts of OSA:
- Daytime Fatigue: Disrupted sleep results in somnolence during the day and negatively affects the quality of life.
- Cognitive Impairment: An individual with OSA may have decreased memory and ability to pay attention, which increases the risk of accidents.
- Metabolic Issues: It results from insulin resistance and obesity, leading to the condition of diabetes type 2.
- Mood Disorders: As a result of unhealthy sleep, an individual may experience stress associated with the effects of sleep deprivation, which contributes to anxiety and depression.
Cardiovascular Problems
Snoring and OSA are closely related to cardiovascular health. The repeated drops in oxygen levels associated with OSA can lead to significant complications.
Cardiovascular Risks:
- Hypertension: OSA is associated with high blood pressure, which by itself predisposes the patient to heart disease and stroke.
- Heart Disease: The cumulative effects of chronic intermittent hypoxia result in cardiac dilatation and arrhythmias.
- Stroke: Untreated OSA significantly raises the risk of stroke due to reduced blood flow and oxygen delivery to the brain’s vasculature.
- Metabolic Syndrome: The combination of obesity, hypertension, and dyslipidemia linked to OSA heightens cardiovascular risk.
Solutions and Treatments for Snoring
After discovering why people snore, we must find suitable and safe treatment methods. There are several questions about How to stop snoring exercises, how to stop snoring woman, how to stop snoring woman naturally, or how to stop snoring man naturally. You can try several approaches to reduce snoring, including lifestyle changes to address the underlying causes or using supportive medical devices. Here are some specific strategies:
Lifestyle Changes
To help stop snoring , you can make the following lifestyle changes:
- Avoid Alcohol: Refrain from drinking alcohol at least 4 hours before bedtime.
- Weight Management: Lose weight if you are overweight or obese.
- Sleep Position: Sleep on your side instead of your back.
- Avoid Allergens: Avoid snoring triggers, especially if allergies worsen your condition.
See more: Effective Ways to Heal Sleep Apnea Naturally for Better Health
Medical Devices (CPAP Machines)
CPAP machines operate by drawing in air from the surrounding environment, filtering and compressing it before delivering it through a tube to your mask. This continuous airflow gently keeps the tongue, uvula, and soft palate from excessively collapsing into the airway. As a result, your breathing becomes stabilized, snoring decreases, and overall sleep quality improves.
See more: Anti-Snoring Devices – Effective Solutions to Stop Snoring
Surgical Options
In many cases, surgery can effectively reduce snoring and treat obstructive sleep apnea. However, snoring may recur over time. A doctor will conduct an examination to determine the most suitable treatment method for you.
Here are some types of surgeries that a doctor may recommend:
- Palatal Implant Surgery: This involves the insertion of implants into the soft palate to help stiffen the tissue, reducing the likelihood of airway obstruction during sleep.
- Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP): This surgery removes excess tissue from the throat, including the uvula and part of the soft palate, to widen the airway and minimize snoring.
- Maxillomandibular Advancement (MMA): This procedure repositions the upper and lower jaw forward to enlarge the airway, addressing both snoring and obstructive sleep apnea.
- Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation: A device is implanted to stimulate the hypoglossal nerve, which helps to keep the airway open by preventing the tongue from collapsing backward during sleep.
- Hyoid Suspension: This surgery repositions the hyoid bone in the throat to stabilize the airway and reduce the risk of obstruction while sleeping.
Conclusion on the topic why do people snore
In summary, snoring is a common phenomenon caused by various factors such as anatomical structures, lifestyle choices, and health conditions. Understanding the causes of snoring is crucial, as it can indicate serious health issues like obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and cardiovascular disease.
Identifying why do people snore, such as age, muscle tone, sleep position, and substance use habits, helps individuals take proactive measures to reduce snoring. Lifestyle changes can reduce snoring. For those with persistent snoring, medical interventions such as CPAP machines or surgery may be necessary. Addressing snoring improves sleep for the individual and enhances the health of partners and family members, creating a healthier sleep environment.
Visit our website to discover more about managing sleep disorders and their impact on health. Explore expert resources to help you achieve better sleep at night. Or find sleep improvement devices at Cpapdiscount.