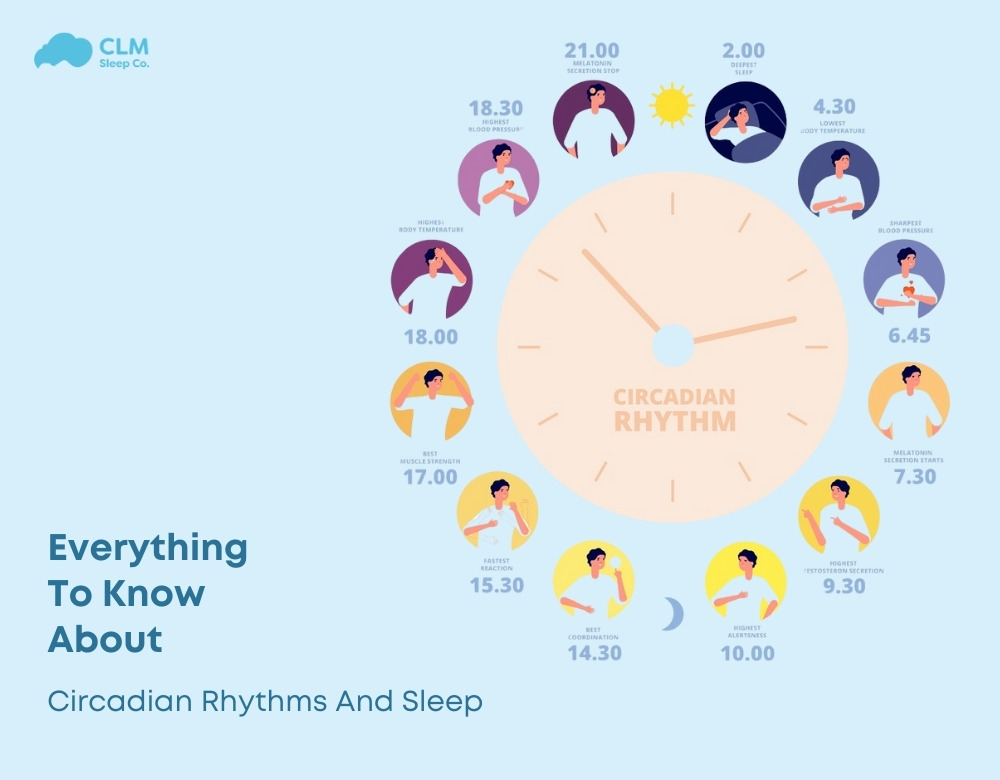
Understanding your circadian rhythm is key to achieving restful sleep and maintaining overall well-being. This internal clock governs essential functions such as the sleep-wake cycle, hormone regulation, and body temperature. When disrupted, it can lead to sleep disorders and other health complications. In this article from CLM Sleep, we’ll dive into how circadian rhythms and sleep are interconnected and share tips on how to keep your rhythm in sync for better sleep.
What is Circadian Rhythm?
Circadian rhythms are cycles of a given duration, typically just over 24 hours, within which phenomena that are ascribed to changes in physiological or psychological state participate. The most notable circadian rhythm is that of sleep and wakefulness. This dominant rhythm also provides periods of clarity and drowsiness both day and night. It is governed by the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of the brain, which responds to environmental signals such as light and temperature.
The circadian cycle thus influences the sleep pattern by indicating the time one should feel awake and the time one should feel drowsy. Proper alignment of this cycle helps in maintaining consistent and restorative patterns of sleep, which is very important for cognitive functioning, stability of mood, and general health.
See more: Circadian Rhythm Disorder
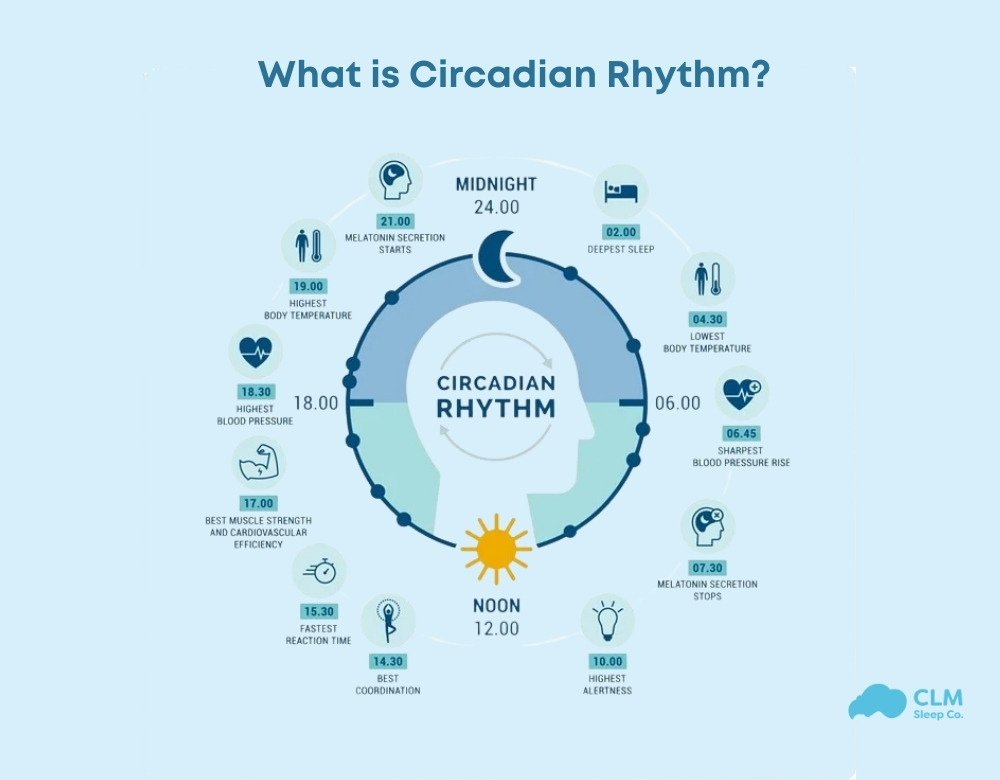
The relationship between circadian rhythm and sleep cycles.
Sleep is structured into multiple cycles, each lasting about 90 minutes, comprising different sleep stages: light sleep, deep sleep, and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. Your circadian rhythm plays a crucial role in ensuring these cycles occur at the right time for optimal rest and recovery.
Melatonin Production and Sleep Timing
Melatonin is the principal sleep hormone and its production by the pineal gland positions this gland as a crucial player in the regulation of sleep. The concentration of melatonin develops in a circadian pattern, with levels naturally rising in the evening, this signals the body that it is time to rest and decreases in the morning to promote wakefulness. Light exposure is a critical determinant of melatonin production – bright light, particularly blue light from screen sources, can inhibit melatonin secretion and thus delay the onset of nighttime sleep
Biological Timing and Sleep Quality
Your circadian rhythm also governs fluctuations in body temperature and hormone secretion. At night, body temperature and blood pressure decrease to prepare the body for sleep, while in the morning, they rise to promote alertness. A well-regulated circadian rhythm ensures these physiological processes align with an optimal sleep schedule.
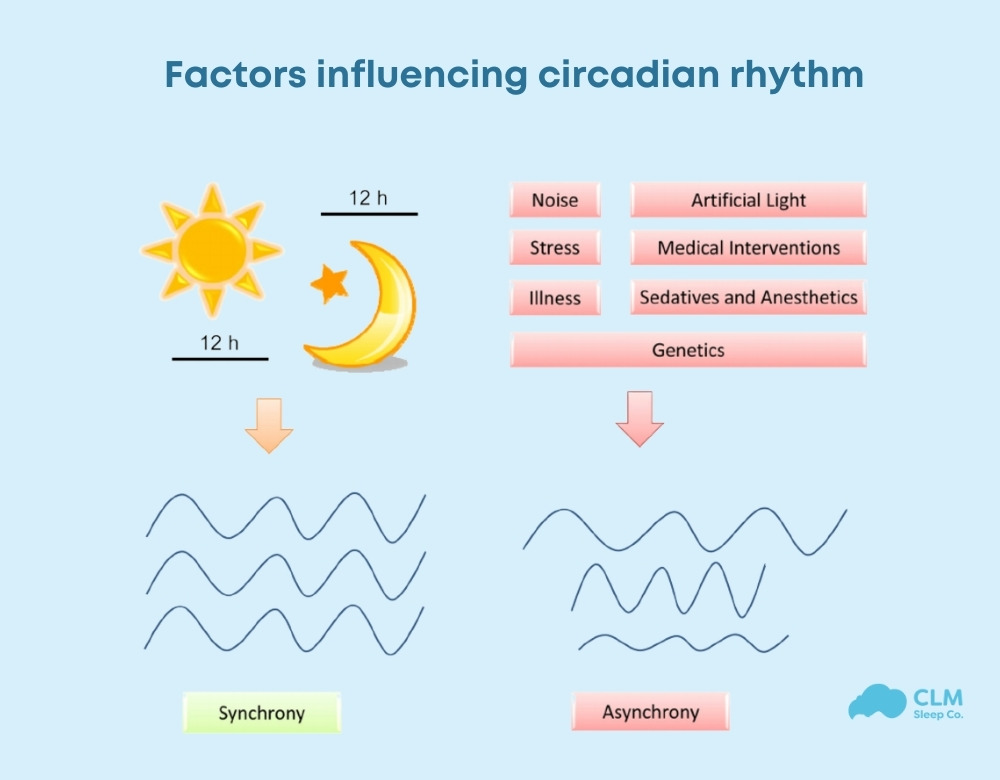
Factors Influencing Circadian Rhythm
Several factors can affect the circadian rhythm:
- Light Exposure: Natural and artificial light exposure, especially during the evening, can shift the circadian rhythm by affecting melatonin production.
- Age: Circadian rhythms can change with age, leading to earlier sleep and wake times in older adults.
- Lifestyle: Irregular sleep schedules, lack of physical activity, and inconsistent meal times can disrupt the circadian rhythm.
- Sleep Disorders: Conditions like insomnia or sleep apnea can interfere with the natural sleep-wake cycle.
Circadian Rhythm and Sleep Disorders
Disruptions in the circadian rhythm can lead to various sleep disorders:
- Insomnia: Difficulty falling or staying asleep can result from a misaligned circadian rhythm.
- Sleep Apnea: Although primarily a breathing disorder, sleep apnea can disrupt the sleep cycle and affect the circadian rhythm.
- Shift Work Disorder: Working non-traditional hours can conflict with the natural circadian rhythm, leading to excessive sleepiness or insomnia.
- Jet Lag: Traveling across time zones can temporarily misalign the circadian rhythm with the local environment, causing sleep disturbances.
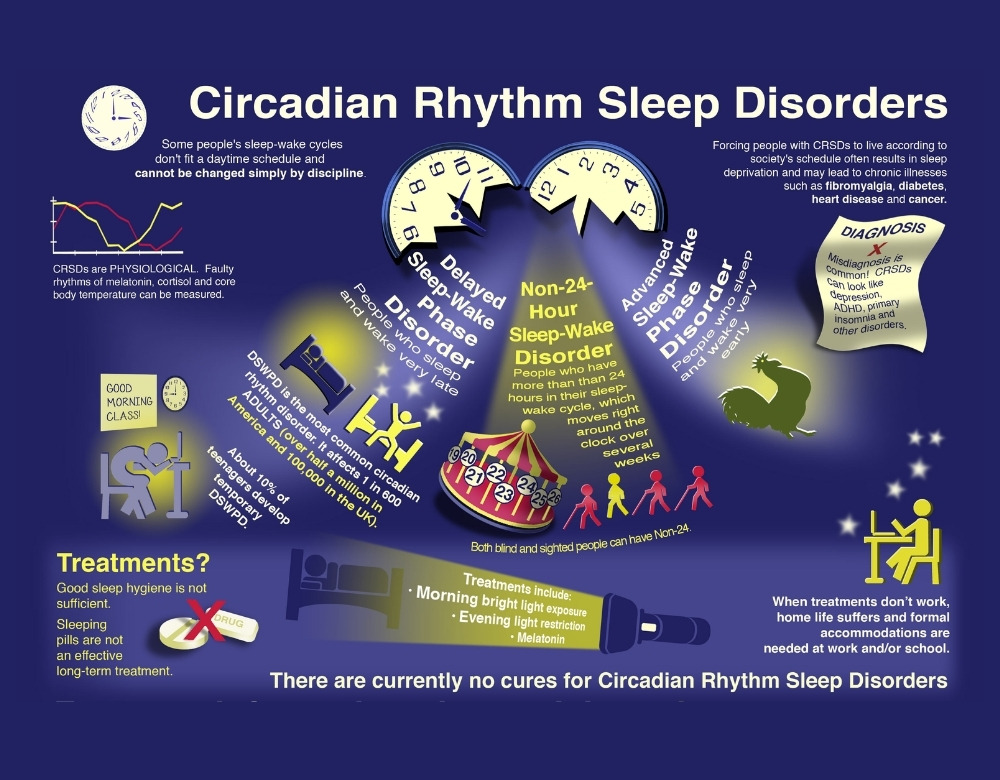
See more: How to fix circadian rhythm
Tips on synchronizing circadian rhythm for better sleep.
Aligning your circadian rhythm with a consistent sleep schedule can improve sleep quality and overall health. Here are some practical strategies:
- Maintain a Consistent Sleep Schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time daily, even on weekends.
- Get Morning Sunlight: Exposure to natural light in the morning helps regulate your internal clock.
- Limit Evening Light Exposure: Reduce screen time and avoid bright artificial light before bed to promote melatonin production.
- Exercise Regularly: Engage in physical activity during the day, but avoid intense workouts close to bedtime.
- Follow Healthy Eating Habits: Eat meals at regular times and avoid heavy meals, caffeine, or alcohol near bedtime.
- Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Engage in calming activities before bed, such as reading or meditation.
- Optimize Your Sleep Environment: Keep your bedroom dark, cool, and quiet to promote restful sleep.

Conclusion of the article
Your circadian rhythm is vital in regulating sleep, energy levels, and overall health. Proper alignment promotes restful sleep, cognitive function, and emotional well-being. However, disruptions caused by factors like light exposure, lifestyle habits, and sleep disorders can lead to poor sleep quality and long-term health issues.
By maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, managing light exposure, staying active, and adopting healthy bedtime routines, you can support a well-balanced circadian rhythm for better sleep.
If you’re struggling with sleep issues, professional guidance can help. CLM’s sleep services offer personalized treatment plans to restore healthy sleep patterns. Additionally, for high-quality CPAP machines and accessories designed to improve sleep health, visit CPAP Discount and explore their range of affordable solutions. Prioritize your sleep – your health depends on it!