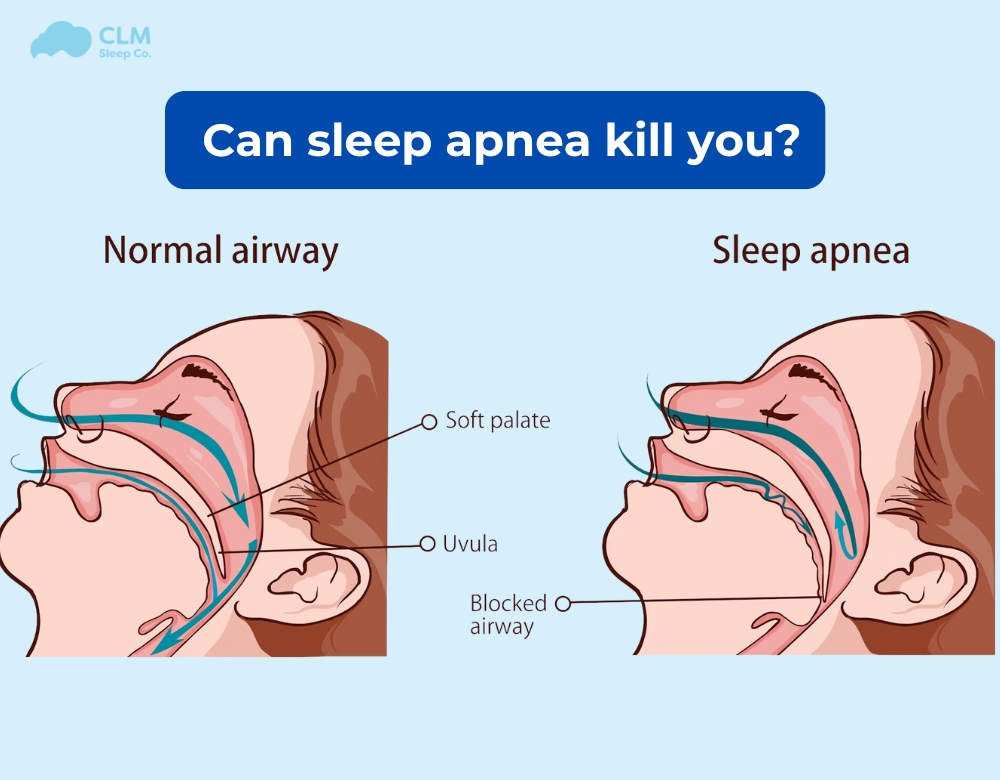
Can sleep apnea kill you? Sleep apnea rarely causes death directly. However, it increases the risk of serious, potentially fatal health conditions, including stroke. Let’s clarify this question together with CML Sleep in the article below!
Is Sleep Apnea Dangerous?
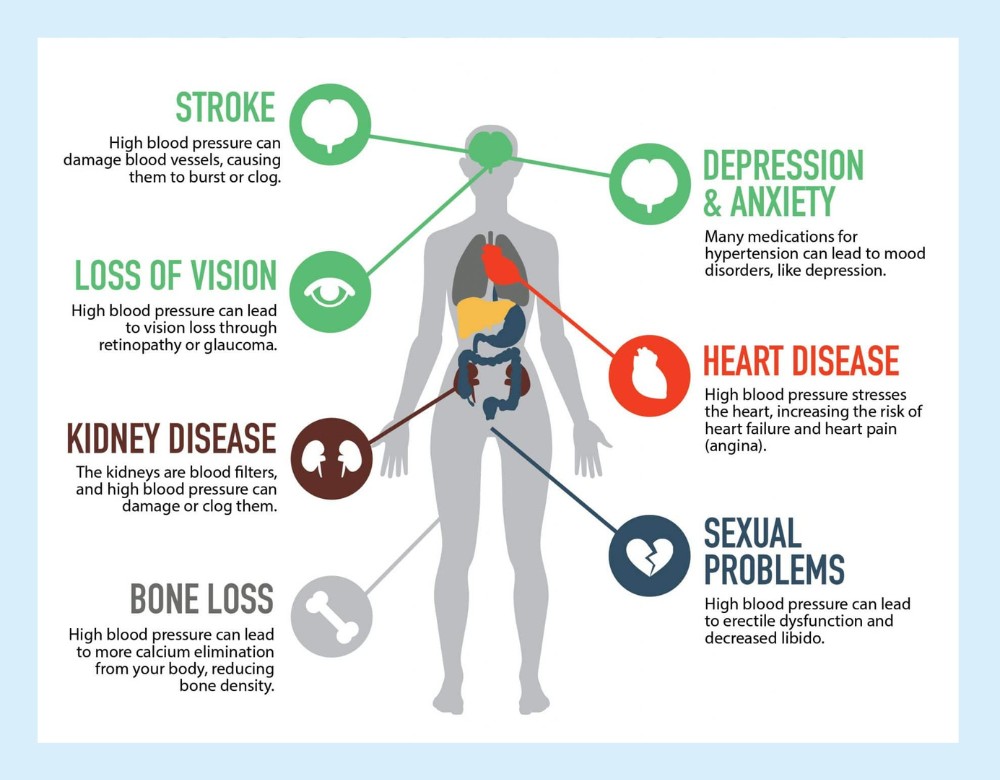
Can sleep apnea kill you? Untreated sleep apnea is associated with various health conditions that can become serious enough to cause death. It involves temporary breathing restrictions during sleep, leading to decreased oxygen levels and increased carbon dioxide. This prompts the sleeper to wake up, but frequent disruptions can contribute to serious health issues. Experts believe repeated airway obstruction can lead to chronic conditions like diabetes, stroke, heart failure, abnormal heart rhythms, and cognitive impairment.
Cardiovascular Problems
Untreated sleep apnea results in increased risks of hypertension, heart disease, and stroke because of the repeated drops in oxygen levels during sleep.
Sleep apnea can cause various cardiovascular problems, such as the following:
- High Blood Pressure: Hypoxemia caused by the nocturnal episodes of breath cessation lowers oxygen levels in the blood, causing a surge in blood pressure, especially during the night. It can chronicle and predispose an individual to CVD (cardiovascular disease).
- Heart Disease: Sleep apnea raises the risks of coronary artery disease and heart failure. This chronic lack of oxygen can cause a buildup of plaque in the arteries and reduce the heart muscle’s efficiency.
- Stroke: High blood pressure and heart disease brought about by sleep apnea raise the probability of getting a stroke. Sleep apnea patients are at a higher likelihood of falling victim to a stroke than those without this condition.
- Heart Failure: Sleep apnea can place a significant strain on the heart, potentially resulting in heart failure, a condition where the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs.
Arrhythmias
Sleep apnea patients often experience arrhythmias, which are irregular heartbeats. This condition is promoted by sleep apnea as one’s blood oxygen levels go down and the carbon dioxide levels go up, which in turn can activate the sympathetic nervous system, increasing the heart rate and, consequently, straining the heart.
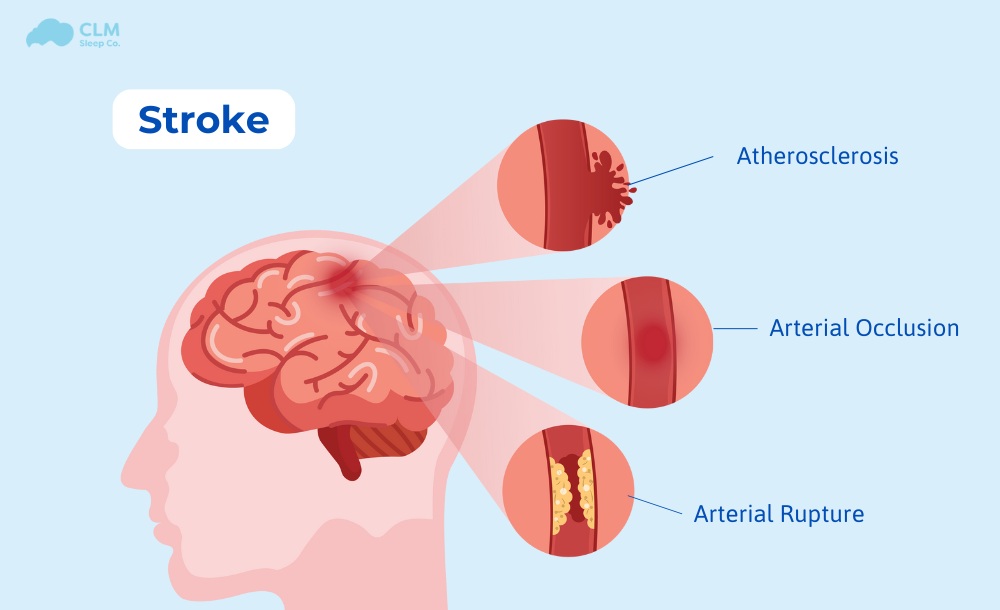
Stroke
Strokes caused by sleep apnea can occur due to several main causes:
- Low oxygen levels: Individuals with sleep apnea may undergo repeated cessations of breathing while sleeping. Consequently, there is a lowering of oxygen content in the blood. Long-term effects of oxygen deprivation are that it can cause damage to blood vessels and other body tissues thereby increasing the risks for stroke.
- High blood pressure: Consequently, sleep apnea consequently results in high blood pressure. Long-term elevation in blood pressure damages blood vessels in the brain, creating an environment suitable for clot formation, an event that causes stroke.
- Arrhythmia: Sleep apnea can cause irregular heartbeats (arrhythmia). These changes increase the risk of stroke.
- Chronic inflammation: Sleep apnea causes chronic inflammation; such inflammation paves the way for diseased blood vessels, hence making their contribution to raising stroke risks obvious.
- Weight gain and obesity: Since sleep apnea is likely to occur in persons who are obese or overweight, this factor further contributes to the increased probability of stroke, just like every other heart disease.
- Increased stress levels: Insufficient sleep and frequent waking produce stress hormones that lead to tiredness and, in turn, raise the likelihood of more severe health outcomes, including stroke.
Accidents (Daytime Fatigue)
Accidents (Daytime Fatigue): Individuals with sleep apnea very frequently experience daytime drowsiness. due to irregular sleep. Here are some of the ways sleep apnea can cause fatigue:
- Driving Accidents: Poor sleep makes you lose focus and make misplaced judgments, thus causing traffic accidents
- Workplace Accidents: Fatigue can lead to decreased productivity and an increased risk of errors or accidents at work, especially in jobs that require a high level of concentration or physical activity.
- Home Accidents: Daytime sleepiness can lead to distractions at home, increasing the risk of accidents, such as falls or misuse of tools.

Pulmonary hypertension
Sleep apnea may increase the risk of pulmonary hypertension. As breathing during sleep is blocked, the oxygen in the blood drops and exerts pressure on the blood vessels of the lungs. Prolonged hypoxia can cause the blood vessels in the lungs to constrict and so raise pressure in the pulmonary arterial system. Special problems can occur if this is not treated properly, leading to breathing difficulties, heart failure, and other serious health issues.
Diabetes
Another danger is diabetes. Studies have even demonstrated that sleep apnea can exacerbate insulin resistance, which is one of the primary causes of type 2 diabetes. Hormone disruptions related to sleep deprivation and obstructive sleep apnea can increase hunger, or at least seem that way, as well as raise blood sugar, which translates to weight gain and a greater risk factor for diabetes. High levels of blood sugar in the body are responsible for a variety of complications.

Liver Issues
Liver failure may develop as well. People suffering from sleep apnea can have a higher likelihood of experiencing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). When we do not sleep properly, the liver can become inflamed and also damaged if there is little oxygen in our body. This, in turn, can cause serious complications and increase the risk of liver disease.
Mental Health Impact
Lastly, sleep apnea can greatly affect our mental health. It causes psychological disorders such as depression or anxiety due to the chronic lack of sleep and daytime fatigue. Lack of sleep leads to stress, affects concentration skills, it leads to reduced performance (at your work and at sports as well), and thus significantly impairs the quality of life. It is essential to catch sleep apnea early to protect both your overall health and prevent dangerous complications.

Short-Term Risks
Sleep apnea can cause serious short-term risks, including the onset of arrhythmias and increased risk of conditions such as atrial fibrillation, heart attack, and stroke. These events are more likely to occur in the early morning, coinciding with REM sleep, when more apnea episodes occur. Studies show that people with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) are 2.5 times more likely to die suddenly while sleeping, especially between midnight and 6 a.m.
Fortunately, treatment options such as continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machines and dental appliances can significantly reduce the risk of these serious complications, including long-term heart problems.
Chronic Risks
Long-term sleep disorders, such as obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), can have significant health consequences. Evidence suggests that the condition increases the risk of high blood pressure, diabetes, and heart disease. It can also lead to depression, memory problems, and increased daytime sleepiness, which increases the risk of accidents.
Although OSA itself is not directly fatal, the complications it causes can be life-threatening. This makes treating sleep apnea essential to protect overall health and prevent serious chronic conditions.
Long-term sleep disorders, such as obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), can have significant health consequences
What are the signs of sleep apnea?
The signs of sleep apnea can vary, but some of the most common signs include:
- Loud snoring: Loud and frequent snoring, especially when interrupted by pauses in breathing, is a key sign.
- Gasping or choking during sleep: People with sleep apnea often gasp or choke when they wake up briefly to start breathing again.
- Pauses in breathing: A partner may notice this when they notice periods of stopping breathing and then resuming.
- Excessive daytime sleepiness: Feeling extremely tired during the day, even after a full night’s sleep, is a key symptom.
- Morning headaches: Frequent headaches, especially upon waking, can be a sign of disrupted sleep due to low oxygen levels.
- Dry mouth or sore throat: Waking up with a dry mouth or sore throat can be caused by mouth breathing while sleeping, which is common in sleep apnea.
- Difficulty concentrating: Constant fatigue due to poor sleep quality can lead to problems with concentration or memory.
- Irritability or mood swings: The effects of sleep loss can affect mood and cause irritability, depression, or anxiety.
Sleep Apnea test
Sleep studies or electroencephalograms are often used to diagnose sleep apnea. There are two common ways to test for sleep apnea:
- Laboratory sleep study (EEG): This is done overnight at a sleep clinic, where medical professionals monitor your breathing patterns, oxygen levels, heart rate, and brain activity while you sleep.
- Home sleep apnea test (HSAT): A more convenient and portable option, in which you wear a monitoring device at home to record data such as breathing effort, airflow, and blood oxygen levels while you sleep.
Both tests can confirm whether sleep apnea is present and how severe it is. If diagnosed, treatment options such as a CPAP machine or lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risks associated with sleep apnea.
When to See a Doctor
You should consult a doctor if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Loud, chronic snoring with pauses in breathing.
- Gasping or choking during sleep.
- Excessive daytime sleepiness or fatigue.
- Frequent morning headaches or waking up with a dry mouth or sore throat.
- Difficulty concentrating or memory problems.
- Mood changes, irritability, or depression.
Additionally, if you have risk factors such as obesity, a family history of sleep apnea, or high blood pressure, it’s important to be vigilant. Early diagnosis and treatment, such as the use of a CPAP machine, can help manage the condition and reduce the risk of serious complications.
Treatment Options for Sleep Apnea
Can sleep apnea be cured? Sleep apnea can be successfully cured! Here are some tips to improve sleep apnea:
- Behavioral Changes: Weight loss, avoiding alcohol, quitting smoking, and establishing a regular sleep routine.
- Sleep Position Changes: Sleeping on your side instead of your back can reduce symptoms.
- CPAP Therapy: A mask delivers continuous air pressure to keep the airway open during sleep.
- Oral Appliances: Devices worn in the mouth to reposition the jaw and tongue, ideal for mild to moderate cases.
- Upper Airway Surgery: Surgical procedures to remove or reduce throat tissue blocking the airway, are considered when other treatments fail.
Conclusion of the article
While sleep apnea may not directly cause death, it increases the risk of serious conditions like heart disease, stroke, and high blood pressure. Treatment options such as CPAP therapy and lifestyle changes can help manage the condition and prevent complications. If you experience symptoms, it’s important to seek medical advice early.
Visit our website to explore more about managing sleep disorders and their impact on health. Discover additional resources from experts to help you achieve better sleep at night. At the same time, choose high-quality sleep apnea treatment devices that are suitable for each individual and come from well-known brands such as ResMed, F&P, Phillips, etc. Check out CPAP Adelaide and and shop our Cpapdiscount online store.