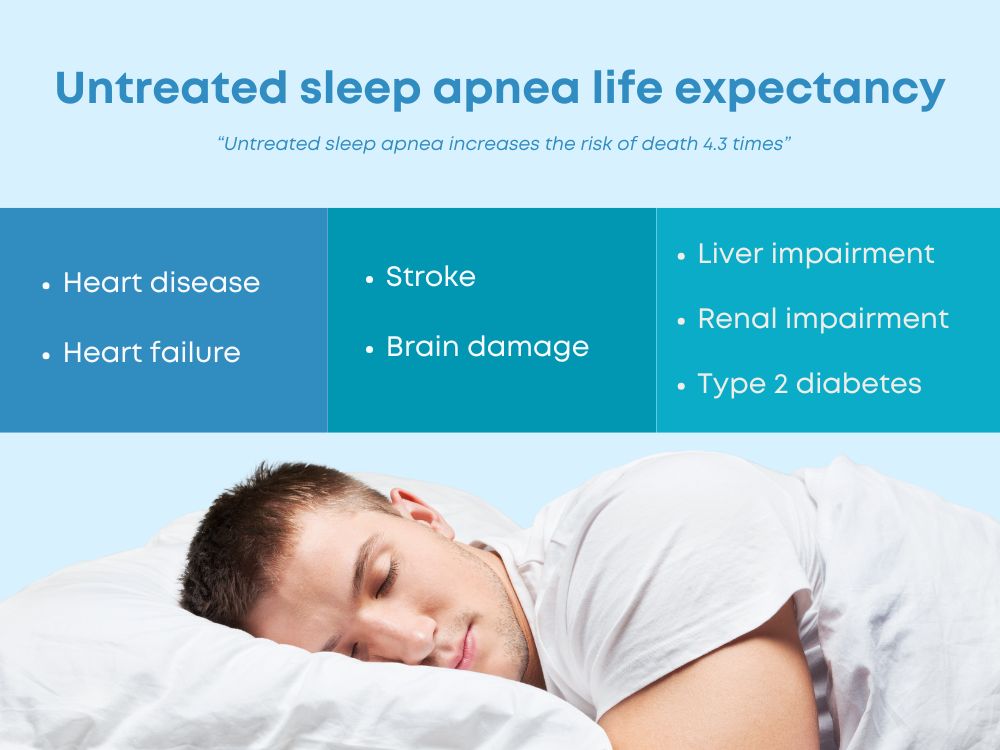
Aside from being a nighttime nuisance, untreated sleep apnea life expectancy is something very serious because this condition poses major health risks that could potentially shorten the span of life. Studies have shown that persons with untreated sleep apnea may have a 4.3 times higher risk of death due to its complications, including cardiovascular disease, stroke, and metabolic disorders. If the oxygen deprivation is prolonged, there’s damage in the heart, the brain, and other important organs, leading to prolonged injury. Fortunately, interventions undertaken early on in the diagnosis, including CPAP therapy and lifestyle changes, go a long way in alleviating these challenges. Knowing the dangers of untreated sleep apnea life expectancy comes as a first step toward sleeping better and leading a longer, healthier life.
Studies have shown that individuals with untreated sleep apnea may have a 4.3 times higher risk of death due to its complications, including cardiovascular disease, stroke, and metabolic disorders.
About Sleep Apnea
A serious sleeping disorder in which a person’s breathing is continually interrupted during sleep is sleep apnea. These interruptions termed apneas-are episodes that last for a few seconds to a minute and can recur many times during the hour. If untreated, sleep apnea can inflict harsh health conditions and reduce both quality of life and life expectancy with untreated sleep apnea untreated sleep apnea.
Common Symptoms of Sleep Apnea
Some common symptoms of sleep apnea include:
- Loud and chronic snoring
- Gasping and choking while asleep
- Excessive daytime drowsiness (EDD)
- Headaches in the morning
- Difficulty concentrating
- Irritable and moody
- Hypertension
Most people suffering from sleep apnea may not know about their condition until their partner, family member, or roommate shines a light on the same.
See more: Excessive Daytime Sleepiness
How to Determine if You Have Sleep Apnea
If you suspect that you suffer from sleep apnea, you must undergo a sleep study for accurate diagnosis. There are two main types of sleep studies:
- In-Lab Sleep Study (Polysomnography): This is carried out in a specialized sleep center or hospital. It monitors brain activity, levels of oxygen, heart rate, breathing patterns, and movements of the limbs during sleep. This study provides the most thorough approach to the evaluation of an individual’s sleep apnea severity.
- At-Home Sleep Study: A more convenient and less expensive option, this test uses an inexpensive portable device that can be utilized to monitor breathing patterns, oxygen levels, and heart rate while the patient sleeps at home. While it lacks the depth of an in-lab study, it can at least help confirm or rule out moderate to severe sleep apnea.
How Does Untreated Sleep Apnea Affect Life Expectancy?
Untreated sleep apnea adversely affects general health and decreases life span. Studies have indicated that people suffering from untreated sleep apnea have an increased risk of developing life-threatening illnesses. The American Academy of Sleep Medicine notes that risk of death is increased by 17% due to several short and long-term health complications associated with untreated sleep apnea. On a repeated basis, chronic sleep apnea risks develop large stress on the cardiovascular systems and disrupts metabolic functioning by reducing levels of oxygen in the body, therefore leading to various kinds of health complications.
See more: Can Sleep Apnea Kill You? Risks and Consequences
Cardiovascular Diseases
Incidentally, untreated sleep apnea subjects the human body to cardiovascular diseases. Breathing is interrupted several times and blood oxygen levels fluctuate, which could temporarily raise blood pressure and increase susceptibility to heart disease, stroke, and heart failure.
- Studies show the risk of high blood pressure in people suffering from sleep apnea is doubled.
- The risk of having a heart attack increases by 30% to 50% in untreated sleep apnea.
- Associating sleep apnea with stroke risk creates a 60% higher risk, with the brain suffering from intermittent oxygen supply.
Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia (Persistent Oxygen Deprivation)
Chronic intermittent hypoxia means that oxygen in the body drops every now and then due to repeated pauses in breathing. Some of the way in which this sets in include:
- Brain damage, which includes memory loss, impairing cognition, and increasing the risk of dementia.
- Impaired cardiovascular functioning which means irregular heartbeat and increased heart failure
- Chronic organ damage including kidney and liver injury as a result of continued oxygen deprivation.
- Damage to the lung systems will predispose an individual to respiratory infections or chronic conditions like COPD.
Metabolic Disorders
Sleep apnea has a strong connection with metabolic disorders, including obesity and type 2 diabetes. Disrupted sleep patterns and oxygen deprivation interfere with the body’s ability to regulate glucose and insulin levels.
- Individuals with sleep apnea are more likely to develop insulin resistance, a precursor to diabetes.
- Studies indicate that up to 80% of people with type 2 diabetes also have sleep apnea.
- Untreated sleep apnea can contribute to weight gain, making it harder to manage obesity-related health issues.
See more: Can sleep apnea cause weight gain?
How Is Sleep Apnea Treated?
Fortunately, sleep apnea can be managed. Sleep apnea treatment options focus on improving breathing, reduction of symptoms, and lowering of severe complications may be applied.
Lifestyle Changes
Very little changes may significantly impact the mild sleep apnea situation.
- Maintaining a healthy weight to eliminate any possibility of airway obstruction.
- Alcohol and sedatives should be avoided because they decrease the muscle tone in the throat, which can be worse for the episodes of apneas.
- Sleeping in a side position, rather than on the back will help to keep the airway open.
- Having a regular sleep schedule is important, as it enhances overall sleep quality.
See more: Effective Ways to Heal Sleep Apnea Naturally for Better Health
Oral Appliances
Mandibular advancement devices (MAD) or other oral appliances help reposition the jaw or tongue to keep the airway open during sleep. Oral appliance therapy is a particularly useful treatment for patients with mild to moderate sleep apnea who cannot tolerate CPAP therapy.
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Therapy
CPAP therapy is the gold standard for moderate-to-severe sleep apnea treatment. This machine blows a continuous stream of air through the mask that keeps the airway open, thereby preventing breathing interruptions. The potential advantages of CPAP therapy include:
- Improved sleep quality
- Reduced risk of heart disease and stroke
- Lowered blood pressure
- Increased daytime energy and mental clarity
To determine the severity of sleep apnea, you need to measure the AHI
Conclusion
Untreated sleep apnea poses serious health risks and can significantly reduce life expectancy. This condition impacts multiple organ systems and overall well-being, from cardiovascular diseases to metabolic disorders. However, effective treatments, including lifestyle changes, oral appliances, and CPAP therapy, can help manage sleep apnea and improve quality of life. If you suspect that you have sleep apnea, seeking medical evaluation and appropriate treatment can help protect your health and extend your lifespan. Visit CLM Sleep to learn more about sleep apnea treatment options and take the first step toward better sleep and overall health.
Source
- American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM) 2020, ‘Study shows that people with sleep apnea have a high risk of death‘, AASM, <https://aasm.org/study-shows-that-people-with-sleep-apnea-have-a-high-risk-of-death/ >.
- National Library of Medicine (2008),’Sleep Disordered Breathing and Mortality: Eighteen-Year Follow-up of the Wisconsin Sleep Cohort’, NLM, <https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2542952/>